Table of Contents
If you’re wondering, “How does Suboxone work?” you’re in the right place. Suboxone is a medication that has brought hope to many people struggling with opioid addiction. It eases the symptoms of withdrawal, lessens cravings, and promotes healing. How Does Suboxone Work? This article will explain how Suboxone works, the science behind it, and its impact on addiction treatment. By the end, you’ll understand why this medication is considered life-changing for those battling opioid dependency.

What is Suboxone?
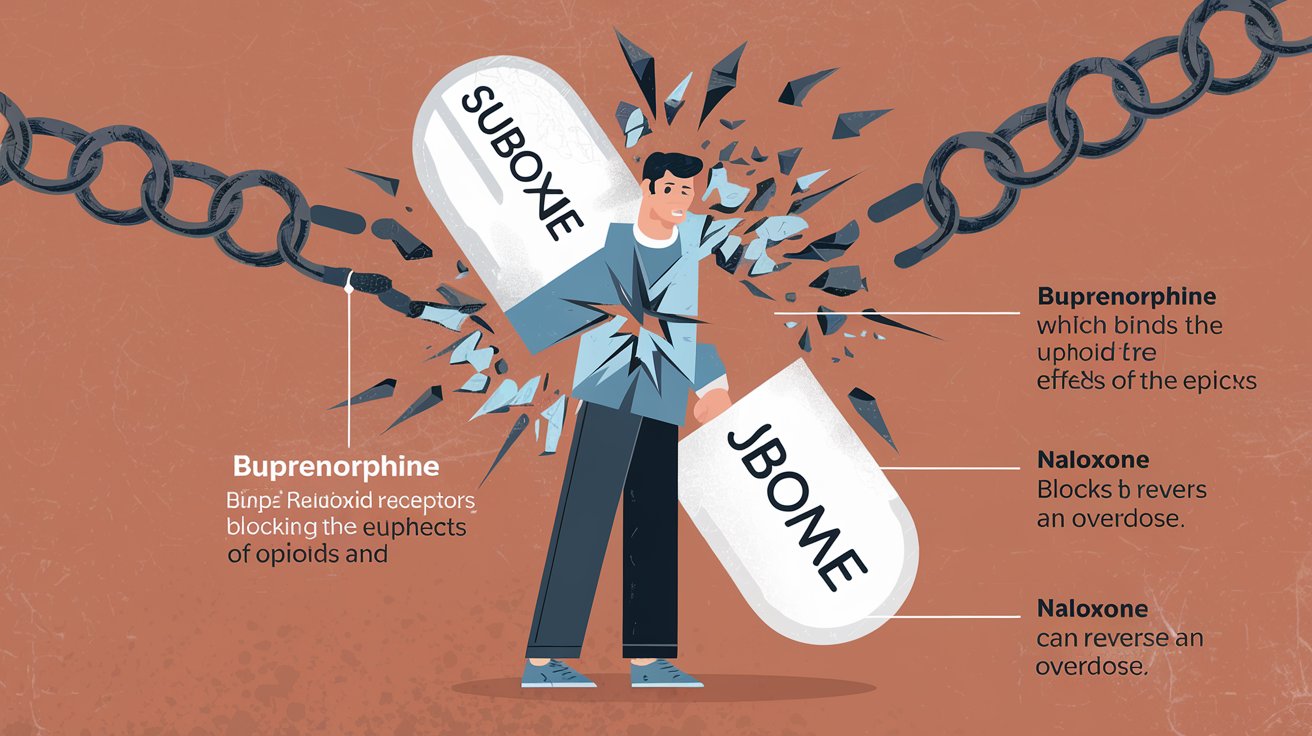
How Does Suboxone Work? It’s essential to grasp what Suboxone is before delving into how it functions. Its two main constituents are naloxone and buprenorphine. These two components work together to help people manage opioid withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings, making it easier to overcome addiction.
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, which means it binds to the same receptors in the brain as opioids like heroin or prescription painkillers but without producing the intense “high.” This makes it practical for reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms without causing full opioid effects.
Naloxone
Naloxone, the second component, is an opioid antagonist. Its primary role in Suboxone is to block the effects of opioids, which helps prevent misuse of the medication. Naloxone will cause withdrawal symptoms if someone tries to inject Suboxone improperly, discouraging overuse.
How Does Suboxone Work in the Brain?
To fully understand “how does Suboxone work,” we must explore how it interacts with the brain. Opioid addiction alters the brain’s chemistry by affecting the opioid receptors, which control feelings of pain and pleasure. When someone becomes addicted to opioids, these receptors crave constant stimulation, leading to dependency.
Buprenorphine and Opioid Receptors
Buprenorphine works by attaching to the brain’s opioid receptors but does so less intensely than full opioids. This helps relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduces the cravings without causing the euphoric high that opioids typically produce. Essentially, buprenorphine “tricks” the brain into thinking it’s receiving opioids, allowing the person to avoid withdrawal symptoms while slowly reducing their dependence.
Naloxone’s Role in Preventing Misuse
Naloxone ensures the medication is used correctly. When taken as prescribed (under the tongue), naloxone remains inactive. However, if someone attempts to misuse Suboxone by injecting it, naloxone blocks the opioid receptors and triggers immediate withdrawal symptoms. This discourages misuse and helps ensure that Suboxone is used only as intended.
Also read: How Much Does a Hair Transplant Cost? Shocking Price Breakdown
What Happens When You Take Suboxone?
How Does Suboxone Work? Now that you understand how Suboxone works let’s explore what happens when someone takes the medication.
Relief from Withdrawal Symptoms
One of the critical benefits of Suboxone is its ability to relieve opioid withdrawal symptoms. People recovering from opioid addiction often face severe symptoms like anxiety, nausea, muscle aches, and cravings. Suboxone helps to ease these symptoms, making it more manageable to go through the early stages of recovery.
Reduction in Cravings
Cravings are one of the most challenging aspects of overcoming addiction. Suboxone works by reducing these cravings, helping people focus on their recovery without the constant desire for opioids. This effect makes Suboxone a valuable tool for long-term treatment.
Safe and Controlled Withdrawal
Suboxone allows individuals to wean off opioids under medical supervision safely. Because buprenorphine only partially stimulates opioid receptors, the transition is smoother compared to quitting opioids abruptly. This supervised withdrawal dramatically decreases the chance of relapsing.
How is Suboxone Administered?
Suboxone is typically taken as a film or tablet that dissolves under the tongue. How Does Suboxone Work? It’s essential to take the medication exactly as prescribed to ensure it works effectively and to avoid potential misuse.
Initial Dosing
When someone begins treatment with Suboxone, a doctor will carefully determine the correct dosage based on the person’s history with opioids. The first dose is usually administered in a clinical setting to monitor how the body reacts to the medication.
Maintenance Dosing
Once the correct dose is established, people move to the maintenance phase, where they take Suboxone regularly to manage cravings and withdrawal. Over time, the dose may be reduced as the person continues their recovery, though some may stay on Suboxone longer as part of a long-term treatment plan.
Suboxone as Part of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
While Suboxone is highly effective in managing opioid addiction, it works best when combined with other treatments. Here’s why Suboxone is usually part of a broader recovery plan.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Suboxone is often used in Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT), a comprehensive approach that combines medication with counseling and behavioral therapies. This combination is considered the gold standard for treating opioid addiction because it addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction.
Behavioral Therapy and Counseling
Therapy and counseling are essential components of recovery. How Does Suboxone Work? While Suboxone helps manage the physical dependence on opioids, therapy helps address the underlying behaviors and emotional struggles that contribute to addiction. Counseling also provides the skills to manage triggers, prevent relapse, and build a healthier life.
Potential Side Effects of Suboxone
Like all medications, Suboxone can cause side effects. While many tolerate it well, it’s essential for initial reaction.
The Common Side has significant effects.
Some common side effects of Suboxone include:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Constipation
- Insomnia
Usually minor, these adverse effects go away when the body gets used to the medication.
More Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, Suboxone can cause more serious side effects like difficulty breathing, confusion, or severe allergic reactions. Speaking with a healthcare provider if you experience any concerning symptoms is essential.
Is Suboxone Addictive?
How Does Suboxone Work? One common concern is whether Suboxone itself is addictive. While Suboxone contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist, its potential for addiction is much lower than full opioids. When used correctly under medical supervision, the risk of becoming dependent on Suboxone is minimal.
Managing Dependency
If someone takes Suboxone for an extended period, they may develop some physical dependence, but this is different from addiction. Addiction involves compulsive drug-seeking behavior, while dependence can be managed safely by gradually tapering off the medication under a doctor’s guidance.
So, how does Suboxone work? This potent medication helps people overcome opioid addiction by relieving withdrawal symptoms and reducing cravings. Its combination of buprenorphine and naloxone makes it effective in treating addiction while minimizing the risk of misuse. How Does Suboxone Work? By understanding how Suboxone works and how it supports recovery, you can see why it has been life-changing for many.